The concept of a Capability Maturity Model (CMM) originated from a Department of Defense funded study of the process maturity of contracting organizations. The CMM model is divided into five levels of maturity based on the definition of processes, the measurement of processes, and process improvement.
The model has been liberally applied to several areas and it is a helpful guide for organizational self-improvement. Here is a CMM model applied to CRM (Customer Relationship Management) and CX (Customer Experience).
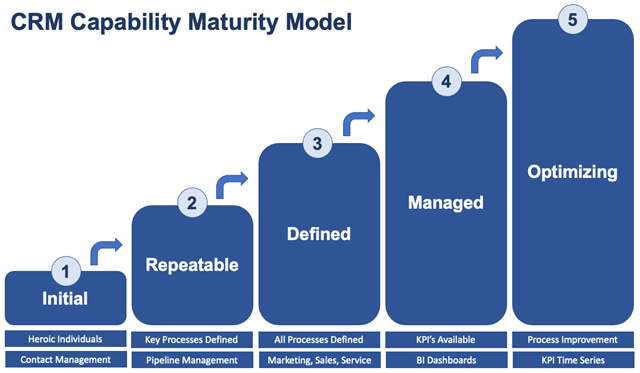
Level 1: Initial (Heroic)
Processes are not documented, and success is only accomplished by the heroic efforts of the individuals involved. The CRM system serves as information storage, a reference database about contacts and accounts, and a log of customer interactions. Typically, smaller sales and marketing organizations fall into this category. The organization can function because teams work closely together and are very skilled. When the organization attempts to scale, it becomes inefficient, and growth is hindered.
Level 2: Repeatable (some processes defined and in effect)
Key revenue growth or retention processes are defined and documented. Usually, the first CRM processes to be defined are the new business development processes such as Lead Qualification or Opportunity Sales Process. Organizations create Lead and Opportunity qualification data points and development status values. Some reports are created to organize the sales pipeline information and the process is followed. The organization can grow faster and more predictably but because other customer experience processes are undocumented, customer retention is inconsistent.
Level 3: Defined (all customer processes defined and in effect)
Process documentation has spread from key processes to all customer experience processes. CRM processes are defined across departments from marketing, to sales, to service. The CRM / CX tools have been deployed across departments on a common platform. Processes are in place to not only acquire new customers but to service and grow them over time. The CRM system can be configured to automate the processes and guide users through process steps. The organization's customer satisfaction and retention improve.
Level 4: Managed (KPI's in place)
Quantitative measurements (KPI's) are applied to the processes to understand how well they are working. Measures such as MQL (Marketing Qualified Lead) and SQL (Sales Qualified Lead), Lead Conversion rates, Opportunity Win Rates, Days to Win, Days in Sales Stage, New Pipeline Creation, Customer Churn Rate, and Net Promoter Score (NPS) are readily reportable from the CRM system and are used to manage the processes. The CRM system or external Business Intelligence (BI) systems provide the rich reporting tools needed. Organizations in this stage start moving ahead of the competition and see improved efficiency in both revenue growth and retention.
Level 5: Optimizing (Continuous Improvement)
KPI's are evaluated and used to improve the underlying processes. Processes are continually evaluated, and changes are tested to see if KPI's can be improved. The CRM / CX system provides the ability to evaluate KPI (Key Performance Indicators) changes over time. Process changes can be made by configuration in the CRM system. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) assist in the interpretation of information and performs optimization work. Organizations reaching this maturity level experience Best in Class results and are significantly more profitable than their peers.
Few of us are able to reach a state of perfection in our personal or organizational lives, but we keep trying! I have found this CMM model both inspiring and humbling but always a good companion on the journey.
Good luck and here at SugarCRM we work to provide you with tools to make it easier to accomplish.
-Christian
